TLS 1.3
TLS 1.3 IP core builds a secure connection between a client and a server over the Internet, enabling high-level security in mission-critical industries and high-volume applications.
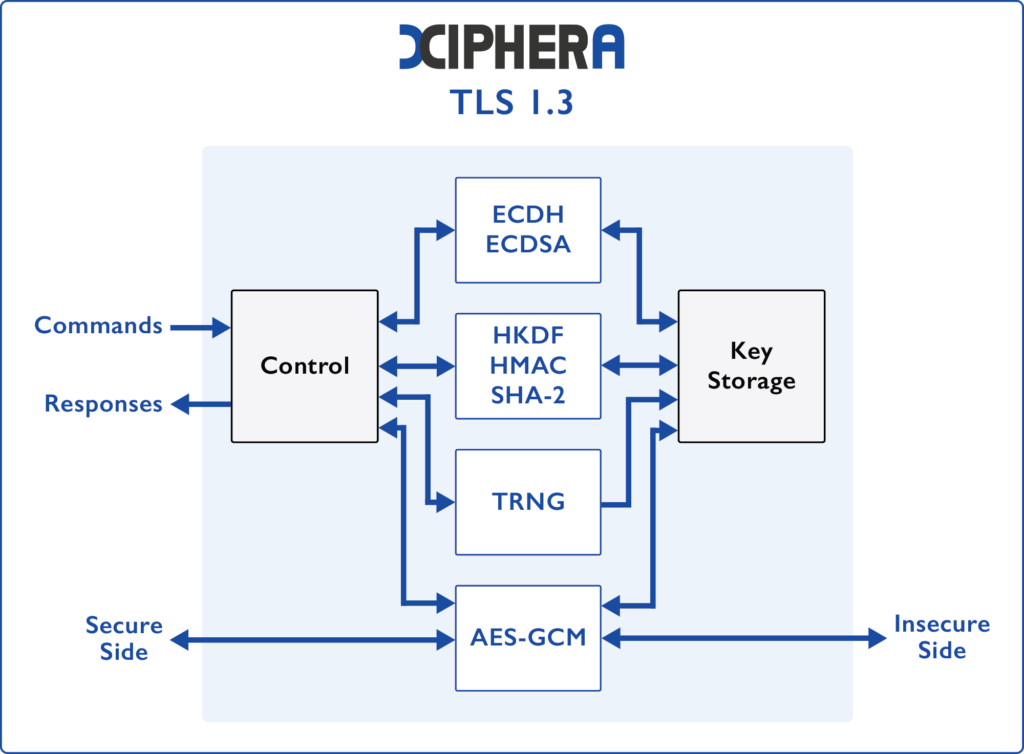
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol used for building a secure connection between a client and a server over the Internet. A hardware-based TLS 1.3 implementation enables high-level security in mission-critical industries, ensuring that security-critical operations are entirely self-reliant on hardware, eliminating the need for software. Despite the extensive feature set, Xiphera TLS 1.3 IP cores maintain a compact footprint, making them exceptionally well-suited for high-volume applications.
Versatile solution for critical network applications...
Industrial automation and communications
Edge computing
System-of-Systems communication
Test & measurement connectivity
Key features
Minimal resource requirements
Optimised performance
Follows RFC 8446 with selected ciphers
Powered by AES256-GCM
Cryptographic operations performed directly in hardware for security and performance
Hardware-based key management
Easy system integration
Vendor agnostic FPGA/ASIC implementation
Technical specifications
The TLS 1.3 IP core is designed to provide robust and efficient security for network communications. This compact solution offers high performance while maintaining minimal resource use, making it the ideal choice for applications where both security and efficiency are essential.
TLS 1.3 AES256-GCM
Product code: XIP7131C
Optimised resource use with less than 20kLUTs, excellent fit for high-volume FPGAs
Over 1 Gbps bulk traffic (client)
For more technical details, including FPGA resources & peak performance as well as ordering instructions, send us a message.
Securing TLS with Post-Quantum Cryptography
The development of quantum computers and security threats it raises are shaping the way we look at cybersecurity and cryptography, including TLS. The security of the TLS Handshake is affected by the quantum threat, making the adoption for PQC algorithms in TLS crucial in the near future.

